Bitcoin often gets most of the attention, but blockchain technology – the system behind digital currencies – is making big changes across many industries that have nothing to do with cryptocurrency.
You can think of blockchain like an engine that isn’t just good for racing but can also be used to power delivery trucks, hospitals, and even elections. This is not just a passing trend; it’s a basic change in how we keep records, build trust, and make processes automatic as more of our lives take place online.
Many industries have trouble building trust and being open between different groups, especially when those groups do not know or trust each other. Usually, they need middlemen like banks, brokers, notaries, or central databases to check and record information or transactions. This adds extra costs, delays, and places where things can go wrong or be tampered with.
Blockchain gives us a different solution. It creates a shared record book, called a distributed ledger, that’s very hard to change or cheat, broadening the applications of blockchain technology in many areas we might not expect.
So, how does blockchain actually help, and why are its effects reaching so many fields outside of cryptocurrency? Let’s look at the basics behind this technology and see how it’s set to change the way we build trust and handle information in the modern day.
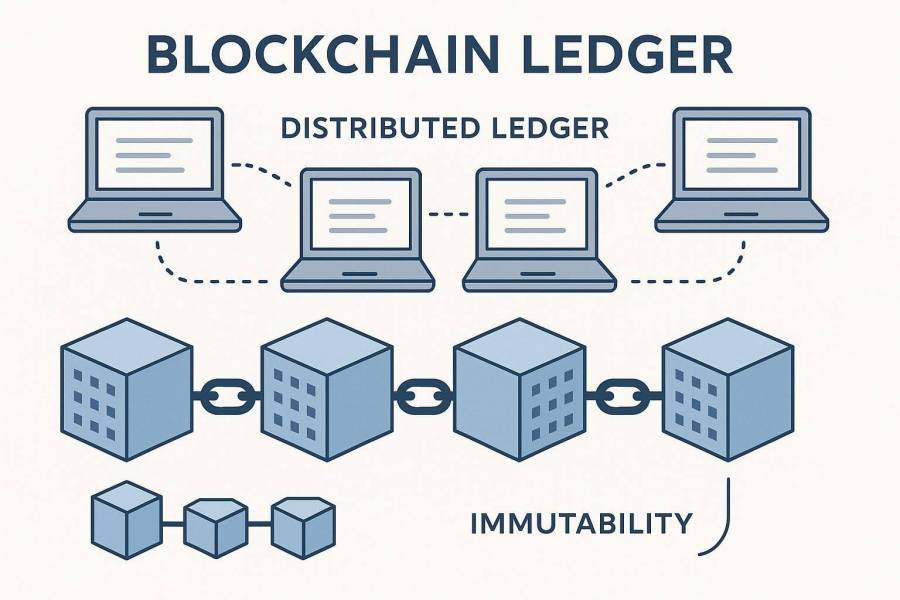
What Is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a digital record book that isn’t kept in one place. Think of it like a spreadsheet that’s copied and shared across a network of computers, called nodes. Each group of new information, or transaction, is bundled into a “block.”
When finished, this block is attached to the block before it, creating a timeline, or “chain,” of blocks – hence, blockchain. This setup stands out from the way old-fashioned databases work. With normal databases, changing a record might only require access to one server.
On a blockchain, to change an old record, you would need to adjust that record, and then every record after it, in every copy spread across many computers. This is nearly impossible to pull off, which makes blockchain very tough against cheating or hacking.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Adding a block to the blockchain involves steps that keep it secure and confirmed by the whole network. When someone wants to record a new transaction, it gets shared with all the nodes. The nodes check the transaction with certain rules.
Before anything is added, the majority of the network must agree, called reaching “consensus.” There are different systems for this – like Proof of Work (PoW) where computers race to solve puzzles (used by Bitcoin), or Proof of Stake (PoS), where computers are chosen to confirm blocks based on how much cryptocurrency they “stake” or own (used by Ethereum now).
Both methods make it extremely difficult for anyone to change the system, since they’d need huge amounts of computer power or currency. After the network agrees and the block is confirmed, it’s attached to the chain, and everyone gets a fresh copy so all records match. That way, each user can be sure their version of the record is the same as everyone else’s.
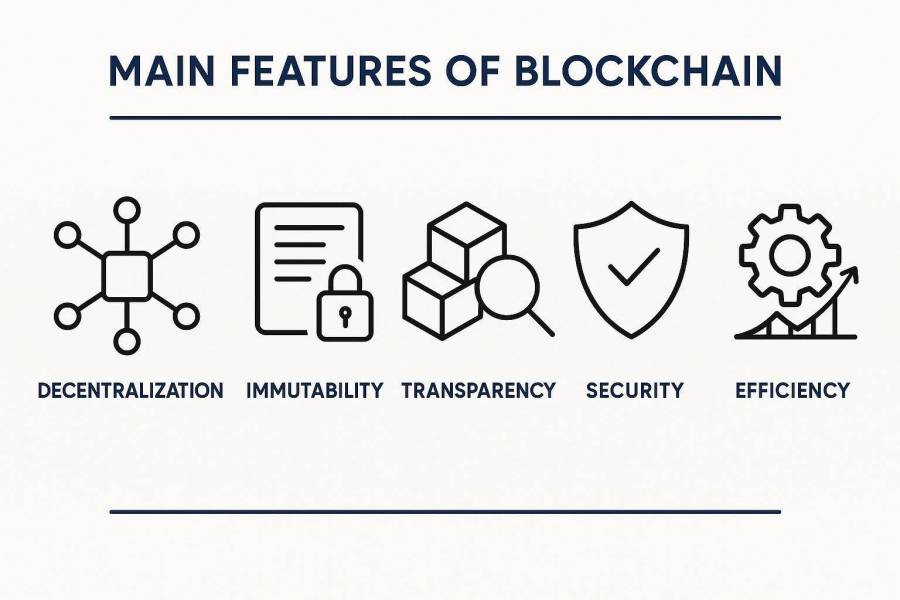
Main Features of Blockchain
Blockchain has some important qualities:
- Decentralization: There’s no central boss, server, or control point. Everything is shared, so there’s no single spot where things can go wrong or be attacked.
- Immutability: Once something is recorded, it can’t be changed or erased. This creates a permanent history – important for auditing or when records must never be altered.
- Transparency: On public blockchains, everyone can see all the transactions (even if they don’t know who made them). This makes it easier for people to trust the system since everyone works from the same information.
- Security: Special codes (cryptography) protect data in each block and connect each block to the next. If someone tries to change a block, it becomes clear to everyone that something is wrong.
- Efficiency: By cutting out middlemen and using smart contracts to automate steps, blockchain can make tasks faster and cheaper. All these features help build trust without needing a single person or company to be in charge.
Why Is Blockchain More Than Just Cryptocurrency?
Many people hear “blockchain” and only think about things like Bitcoin or risky investing. This isn’t strange, as Bitcoin was the first blockchain that many people saw. But focusing only on cryptocurrency is like thinking the internet is just for email – there’s so much more.
Misunderstandings About Blockchain
A common mistake is believing blockchain only exists for digital coins, or that its only use is for payments. In reality, blockchain can securely record and check all kinds of data or transactions, not just money.
Another misunderstanding is thinking only open, public blockchains exist. In truth, blockchains can also be private or shared among certain trusted organisations, allowing different types of use while keeping main benefits like security and honesty.
How Blockchain Creates New Solutions Outside of Crypto
Blockchain can create trust and make things work better where people might not trust each other or where everything usually flows through a central authority. With a shared record everyone can check, and smart contracts that take care of agreements automatically, blockchain can change the way organizations work.
For example, any field with lots of partners, paperwork, or a risk of cheating or errors – like supply chains, medical records, financial settlements, identity checks, or voting – can benefit. Blockchain acts as a single record all authorized users can see, making sure everyone works from the same information, without a central middleman.
How Blockchain Helps With Security, Transparency, and Trust
Now that cyber-attacks and lost trust in major institutions are so common, blockchain offers an alternative for safely sharing important information. It directly deals with problems around data leaks and doubt between participants.
Better Trust in Transactions
Usually, there’s one central group keeping all the records, and everyone has to trust them. Blockchain spreads this trust across the network. Every step is double-checked by many computers, and once it’s written, it becomes part of a record everyone with permission can see. This ensures the truth can’t be changed by one person or group.

Stronger Data Protection and Privacy
Blockchain uses tough security codes to keep data safe and link each block. If anything in an old block changes, its special code changes, which breaks the chain and makes any cheating easy to spot.
On open blockchains, participants often use fake names to protect privacy. On private blockchains, only certain people can view sensitive information, which still stays secure.
Clarity for Auditing and Following Rules
Since all accepted participants can track the whole history on a blockchain, audits are easier and quicker. This helps industries that have to meet legal standards – like finance or healthcare – stay honest and stick to the rules.
What Are Smart Contracts and How Do They Make Business Automatic?
The record-keeping side of blockchain is only one part. Smart contracts are like digital robots that can act when certain conditions are met.
What Is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a computer program that automatically carries out actions when certain things happen. For example, like a vending machine: put in money and make your choice, and it makes the delivery without human help.
Core ideas:
- Automatic: Runs by itself when triggered.
- Trustless: Don’t have to rely on any middleman – the code and blockchain enforce the rules.
- Fixed Rules: Once set up, the rules usually don’t change.
- Efficient: Cuts down on delays and costs by getting rid of manual steps.
Blockchain in Industries Beyond Cryptocurrency
The mix of security, honesty, and automation blockchain offers is finding uses in many industries.
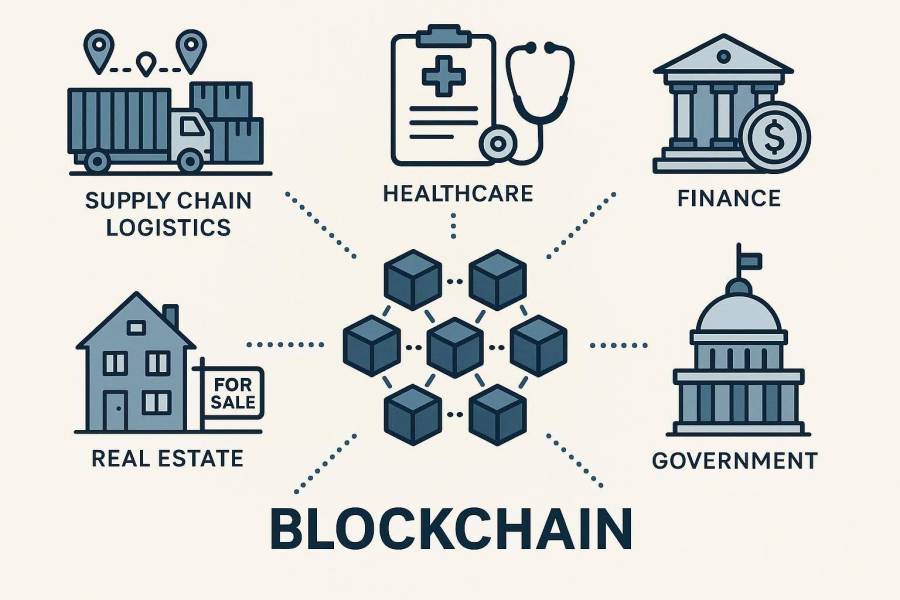
Supply Chain Improvements
Most supply chains have lots of partners across the world, making it hard to track items or check if things are real. Blockchain gives an unchangeable record for each step, like manufacturing and delivery. This makes it much easier to trace products quickly, for example in a food safety scare.
Customers can even scan items to see their whole history, which increases trust. Some organizations, like the UK’s Food Standards Agency, have tried blockchain to track meat as a real-world test.
Securing Healthcare Information
Health systems juggle scattered records, strict privacy laws, and struggles with sharing data. Blockchain can store encrypted records that only the right people can access, with patient approval. This helps hospitals and doctors share information safely and makes it easier to trace drugs and prevent fakes. Some companies are already using blockchain for protected medical records.
Better Finance and Insurance
Blockchain in finance is about much more than digital money. It makes payments faster, cheaper, and clearer by skipping the usual complex routes. New systems allow splitting up assets like real estate into digital pieces that can be traded easily and fairly. Smart contracts handle loans, insurance, and trades automatically. Big banks are already using blockchain to cut paperwork and speed up international deals.
Real Estate Made Easier
Property deals take a long time and need many checks and go-betweens. Blockchain lets people see a full, unchangeable record of who owns what, and smart contracts can handle sales automatically – meaning fewer steps and lower costs.
Government and Public Services
Governments hold lots of sensitive info, from public documents to personal IDs. Blockchain can handle digital ID, voting, and records in a way that’s tamper-proof and gives people more control. Voting on blockchain could reduce cheating and make elections more trustworthy.
Managing Digital Identity
Proving who you are online isn’t always safe. Blockchains let users control their own digital IDs and only share what’s needed. Schools can issue proof of education on the blockchain, and so can other organizations, which makes lies about qualifications much harder.
Retail, Shipping, and Online Markets
Beyond tracing products, blockchain can run loyalty programs and stop fakes in retail. In shipping, it can handle payment and documents without extra paper. In e-commerce, peer-to-peer transactions can go through blockchains safely with fewer fees.
Media, Entertainment, and Copyright
Creative industries struggle with unfair payments and piracy. Blockchain makes ownership clear and ensures payments go out automatically through smart contracts. Tools like NFTs can show proof of ownership and let creators sell work directly to fans.
Education and Diplomas
Fake degrees are a real problem. Schools can give out blockchain-based certificates that are easy to check and hard to fake, letting students share their accomplishments directly and securely.
Benefits and Challenges of Blockchain for Businesses
Businesses looking at blockchain need to think about the pluses and the potential issues.
Making Work Faster and Reducing Costs
Blockchain can speed up processes and cut costs by cutting out middle steps and reducing paperwork. It’s especially useful where there are lots of manual checks or where several groups must agree.
Opening Global Access and New Ideas
With blockchain, even small businesses can reach new markets and work easily with partners worldwide. There are new chances for joining in, like shared ownership of assets and safer digital identity systems.
Barriers to Using Blockchain
- Scaling: Some older blockchains can’t handle many transactions at once, but newer systems are getting faster.
- Energy Use: Some blockchains use lots of electricity. Newer types like Proof of Stake use less.
- Technical Challenges: Setting up a blockchain can need special know-how and doesn’t always fit well with old computer systems.
- Startup Costs: It may be expensive to get started before saving money in the long run.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Rules for blockchain are still changing. Businesses must figure out what laws apply, especially when working across borders. Clearer laws are expected as blockchain use grows, which should help with wider adoption.
Final Thoughts
As we move further into 2025, blockchain’s role goes way beyond its original use in cryptocurrencies. Its main strengths – unchangeable records, openness, and strong security – are shaping the future of how we handle important information and build trust online.
With better, greener systems, a focus on big business needs, and joining with other technologies, blockchain is becoming a key part of digital life.
The way ahead promises more open supply chains, safer sharing of patient data, quicker payments, and stronger control of personal information. There are still challenges, but the drive to solve them and use blockchain’s strengths is strong.
This steady change is already making our digital world safer, faster, and more trustworthy, one block at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Industries Will Be Most Changed by Blockchain?
Industries seeing big impacts are finance, supply chain, healthcare, real estate, and government. But any sector needing honest record-keeping, shared information, or trust between partners can benefit from blockchain.
How Can Small Businesses Use Blockchain?
Small companies can join open or group blockchains for things like tracking goods, joining marketplaces, or managing digital identities. Many tools are now easy to use, letting smaller players get involved without building new blockchains.
What Are the Main Risks?
Some risks are the technical challenge of setting up, some blockchains being slow, changing rules and unclear laws, coding mistakes in smart contracts, and the difficulty in fixing errors once recorded. Electricity use is less of an issue in newer systems.

Peyman Khosravani is a global blockchain and digital transformation expert with a passion for marketing, futuristic ideas, analytics insights, startup businesses, and effective communications. He has extensive experience in blockchain and DeFi projects and is committed to using technology to bring justice and fairness to society and promote freedom. Peyman has worked with international organizations to improve digital transformation strategies and data-gathering strategies that help identify customer touchpoints and sources of data that tell the story of what is happening. With his expertise in blockchain, digital transformation, marketing, analytics insights, startup businesses, and effective communications, Peyman is dedicated to helping businesses succeed in the digital age. He believes that technology can be used as a tool for positive change in the world.








