
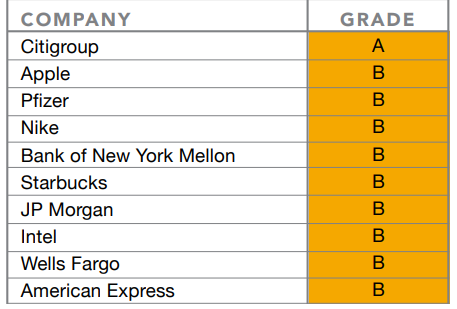
There is still much to do and yesterday’s Equal Pay Day in the US just highlighted how far we are to get a fully equal society. As many other reports out there, a new Arjuna Capital/Proxy Impact report ranked 46 of the world’s largest companies on gender and racial pay equity. Unfortunately, it could only hand out an “A” to one company: Citigroup. A failing grade of “F” is awarded to half (23) of the total group of companies, including banking institutions like Goldman Sachs, tech giants as Oracle, big chains such McDonalds, retailer Walmart, and worldwide hygiene company Colgate.
Nine companies—Apple, Pfizer, Nike, Bank of New York Mellon, Starbucks, JP Morgan, Intel, Wells Fargo, and American Express – garnered a “B” grade for their efforts to disclose and act on their gender pay gap.
The second annual “Gender Pay Scorecard” (GPS) report, published by Arjuna Capital and Proxy Impact, takes a quantitative accounting of current disclosures and goals to help investors navigate best practices on pay equity.
Natasha Lamb, wealth manager and managing partner, Arjuna Capital, and report lead-author, said: “Equal Pay Day is a perfect time to take account of corporate America’s progress toward pay equity. Only one company – Citigroup – earned our highest mark for setting a new standard for gender and racial pay equity disclosure. Pfizer is a fast follower, but it’s time other companies keep pace and hold themselves to a more meaningful standard. Arjuna Capital has pressed 22 major U.S. companies to take critical first steps toward pay equity, but it’s time for Silicon Valley and Wall Street to step up their game.”
Michael Passoff, CEO, Proxy Impact and report co-author added: “Numerous studies show women are paid less than their male counterparts. This is a key challenge for companies as they face reputational risk, consumer backlash, new legislation, and governmental and employee lawsuits. While salary policies can help ensure equal pay for equal work, providing equal opportunity to move up the corporate ladder requires more specific action from management, including better recruitment, development and retention. Ultimately, it is both equal pay and equal opportunity that will eliminate the gender pay gap.”
Key Report Findings
By sector, the highest and lowest-rated companies were:
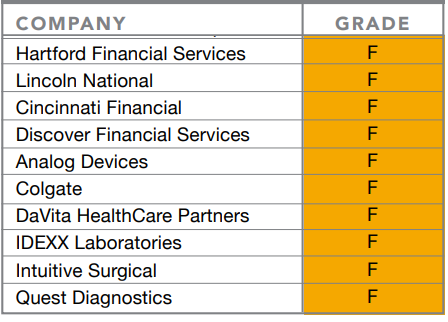
- BANKING/FINANCIAL. Citigroup is the only company to receive an “A,” as the first U.S. company to provide adjusted equal pay and unadjusted median gender and minority pay data on a global basis. Of the 19 financial companies graded, 10 failed: Metlife, Arthur J. Gallagher, Goldman Sachs, Marsh & McLennan, Key Corp, Citizens Financial Group, Hartford Financial Services, Lincoln National, Cincinnati Financial, and Discover Financial Services.
- TECH. Apple and Intel were the only tech companies to earn a “B” grade. Three of 12 technology companies failed: Oracle, Hewlett Packard and Analog Devices.
- RETAIL. Nike and Starbucks led the consumer sector with “B” grades. Five of the nine companies in this category failed: Marriot, McDonald’s, Walmart, TJX Companies (which own TJ Max), and Colgate.
- HEALTH/PHARMA. Pfizer was awarded a “B” for a commitment to report its global gender pay gap and U.S. racial pay gap in 2019. The other five of six healthcare companies received “F” grades: Cigna, DaVita, HealthCare Partners, IDEXX Laboratories, Intuitive Surgical, and Quest Diagnostics.
GPS ranks companies on quantitative pay disclosures (not qualitative assurances), commitments to report pay gap numbers annually, global coverage, and goals. The GPS breaks down this data into a simple rubric to more fully understand company performance and commitments across five categories: (1) equal pay gap; (2) median pay gap; (3) racial pay gap; (4) coverage; and (5) commitment.
The report describes investor engagements, regulatory pressure, and the business case for pay equity—all of which have fundamentally changed the landscape for pay equity over the last five years. GPS also clarifies the difference between company-reported adjusted wage gaps and unadjusted median pay gap disclosures mandated by the United Kingdom. The scorecard was updated to include the median racial pay gap as a new sub-category, bringing the total ranked factors to 10. Women of color have the largest pay gaps illustrating the intersectionality of gender and race.
Shareholder Activism Background
In the last five years, at least 64 companies have faced more than 100 shareholder resolutions on the gender pay gap. In 2015, Arjuna Capital launched the gender pay shareholder campaign when it filed a shareholder proposal with technology firm, eBay. In 2016 Proxy Impact and other investors joined this effort and 11 proposals were filed. The shareholder campaign more than doubled to 26 companies in 2017, expanding into the financial services and retail sectors. Thirty-three proposals were filed in 2018, and 27 so far in 2019, with a new focus on the healthcare sector.
Arjuna Capital continues to lead this effort and has filed a total of 46 proposals at 23 companies in the tech, financial, and consumer sector. 22 of these companies have committed to disclose and close their pay gaps on an adjusted equal pay for equal work basis, an important first step. This year Arjuna is requesting more comprehensive reporting from the companies, and filed a new proposal with 12 companies requesting unadjusted global median gender and U.S. racial pay gap data. This evolution is important because while adjusted data shows if there is equal pay for equal work, unadjusted median pay data shows if there is equal opportunity to high paying jobs.
In February 2019, Arjuna named the 12 top banks and tech giants it is engaging in 2019 with a new median gender and racial pay equity resolution, including Adobe, Amazon, American Express, Bank of America, Bank of New York Mellon, Facebook, Google, Intel, JPMorgan, Mastercard and Wells Fargo.
In January 2019, Citigroup surprised investors when it revealed its “median” or companywide gender pay gap is 29 percent and its minority pay gap is 7 percent, becoming the first U.S. company to respond favorably to Arjuna Capital’s proposal asking for more comprehensive pay equity reporting. A recent oped published by Lamb, describes the importance of this reporting.
A growing number of investor groups have made the healthcare sector a major focus in 2019. Proxy Impact withdrew its resolution at Pfizer when it committed to conduct a global gender pay gap analysis of both adjusted and unadjusted data, and its U.S. racial pay gap in 2019. This is a standard to which we want all companies to move.
HedgeThink.com is the fund industry’s leading news, research and analysis source for individual and institutional accredited investors and professionals








