
Over the years, cybercriminals have become more creative in penetrating systems and more demanding in asking for money. Attacks have cost businesses billions of dollars and the numbers are only expected to go higher.
These costs have driven businesses to invest in reliable cybersecurity companies and implement measures to protect themselves against unwanted attacks and losses. Protecting yourself on the internet entails putting up layers of security measures to make it more difficult for cybercriminals to penetrate.
In this post, we’ll be discussing 7 different cybersecurity practices that you should have to protect your business from cyber attacks.
Let’s get started.
1. Put Up a Firewall
Putting up a firewall is essential in monitoring inbound and outbound network traffic of your website. Ultimately, it prevents unauthorised users from accessing data within your private network. This layer of protection, on top of a reliable Runtime application self protection, blocks malicious websites and malwares that users might unknowingly download.
It can also be programmed to prevent any user from sending out sensitive data from the website’s network. There are two types of firewalls:
Hardware Firewall
A hardware firewall is a layer of protection between computers and the internet. This type of firewall inspects all inbound data. It allows safe data packets to enter and blocks out suspicious ones.
Setting up a hardware firewall requires and controlling it requires an IT department that will thoroughly look after its implementation and maintenance. However, this can be done on a single device.
Software Firewall
This type of firewall is found on individual computers within a network – ideally for employees who work at home. Software firewalls inspect and filter outgoing data from computers. It also blocks out data from programs that have malicious content.
Compared to a hardware firewall, each computer is updated and monitored individually and cannot be controlled from a single device.
2. Install a Reliable Security Software
Having reliable security software — such as anti-virus and anti-malware protection — is one of the most common yet effective cybersecurity practices. A strong security software can detect malicious codes that have slipped through your network and into your devices.
It can effectively detect and remove spam, malware, and viruses even in your emails and downloads. Let’s take a look at this security software as an example.
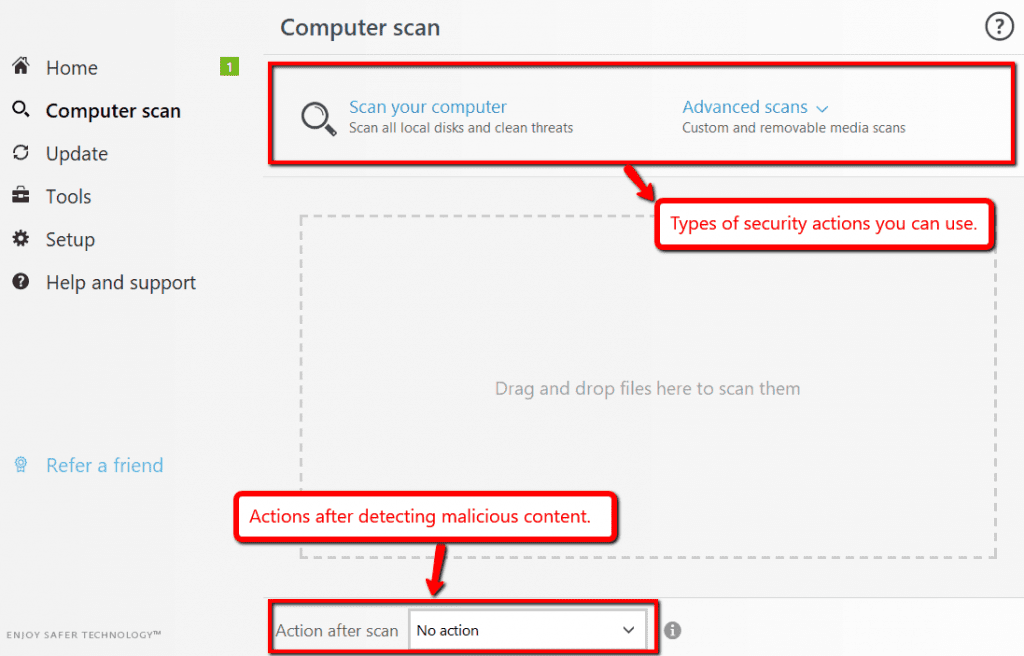
The software allows the user to do several kinds of actions – whether for internal or external device scanning. It also allows the user to decide what to do after the security scan.
3. Approve Software Updates
Cybercriminals have a good habit of checking security weaknesses — especially for outdated software. Software updates can include the repairs of security flaws found in your software programs or operating systems. Ignoring or putting off that update might leave you vulnerable to attacks specifically targeted at that security hole. The attack could come in a code written as a malware.
These attacks could be as simple as ads on a suspicious website or compromised spam messages you accidentally opened. Regardless of its form, attacks can go unnoticed if you fail to update your software on time.
An example of this would be Shipwork’s mandatory software update.
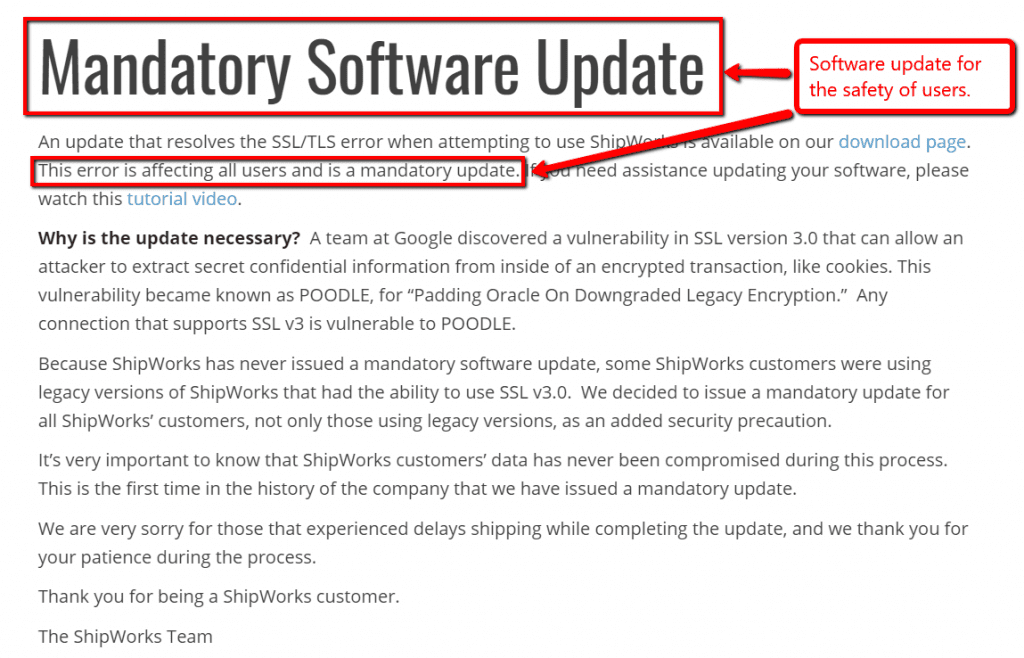
This update resolves the issue for users who have the ability to use SSL v3.0 which is vulnerable to sensitive data breaches. It broadcasted a mandatory update to protect its users from security breaches. No matter how tempting it is to ignore updates — don’t.
4. Check for Vulnerabilities
Ironic as it may sound, penetrating your own website is a good cybersecurity practice. Checking your website’s vulnerabilities is a helpful way of knowing your own weaknesses without actually compromising the entire system.
The good side of this practice is that you can trust who’s penetrating your website and you’ll get a comprehensive report of your website’s vulnerabilities — should there be any. This practice allows you to better understand the cyber security kill chain.
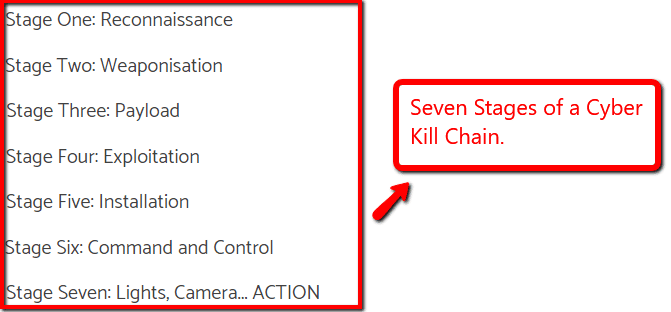
The cyber kill chain includes seven stages.
It starts with cybercriminals scanning for potential weak targets and ends with the planting and execution of malware into systems and devices. Penetration tests follow this structure of a cyber attack to thoroughly assess which stages your application is most vulnerable in.
5. Install Encryption Software
Nowadays, it’s common and convenient for businesses to conduct online transactions. These transactions include sensitive information such as credit card numbers, bank accounts, and even social security numbers — all of which are useful and attractive for cybercriminals.
Dealing with this kind of information, it’s crucial for businesses to utilize an encryption software to alter information into unreadable codes. By altering the information, it will be useful for whoever has it because they won’t have the keys to convert the information.
Besides encryption software, you can go for an SSL certificate that can manage to encrypt the data travels between the server and the browser. If you are looking for such an SSL then, first you need to understand the domain requirement. lets say, if you have subdomains then a cheap ssl wildcard can be useful in this case that allows you to add subdomains in the future without any extra cost. SSL certificate is also mandatory when online transactions or credit and debit card payment is involved.
6. Limit Access to Critical Data
According to Hedgethink, customers in financial sectors are hesitant to share required sensitive information in the fear of data breaches. In order to appease customers, businesses should practice limiting the access of critical data to employees who only need it for their jobs.
Other than that, employees should not be granted any access.
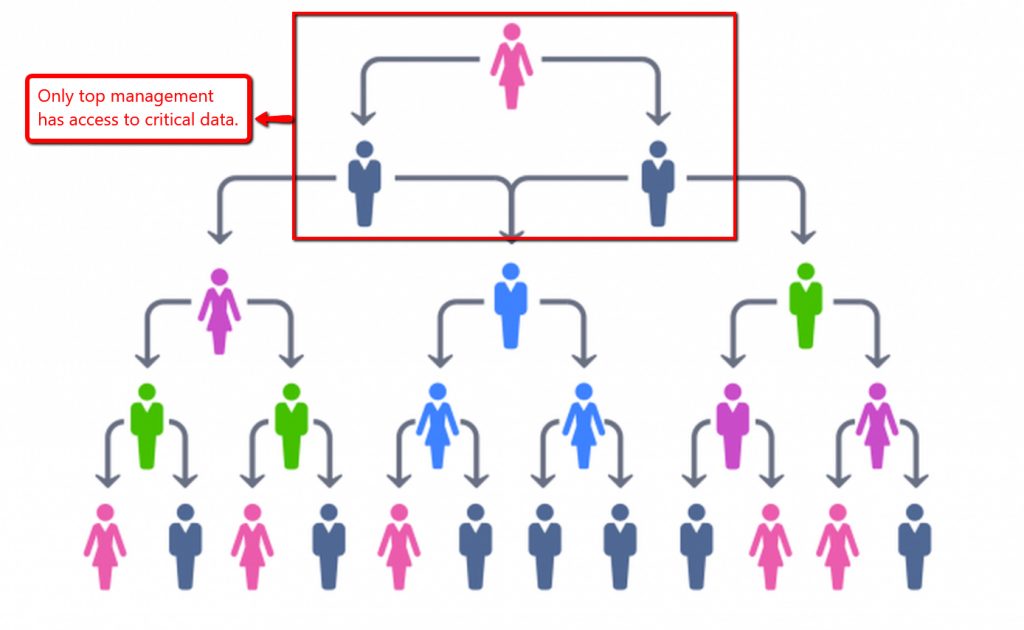
Translating it to a structure, only key employees — such as top management — should have access to critical data. With only a few key employees having access to critical data, accountability can be increased and risk of data breaches can be minimized.
7. Use Complex Passwords and Additional Measures
According to the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, about 80% of hacking-related breaches started with weak and reused passwords. This percentage shows that failure to use complex passwords put businesses at risk.
Using complex passwords and regularly changing them make it difficult for hackers to penetrate websites and make businesses less desirable to attack. In this light, businesses can also utilize artificial intelligence to add security procedures that help make user and employee log-ins more secure and convenient.
Let’s take Paypal log-in as an example.
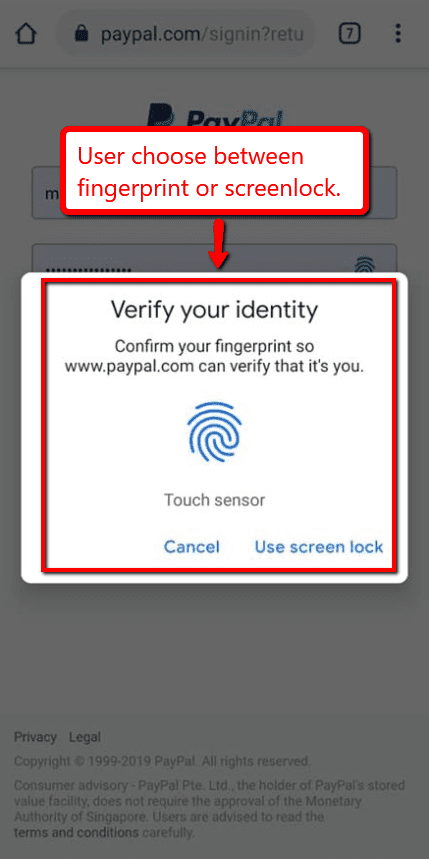
Paypal allows gives its users the option to use a fingerprint scanner every time they wish to log into their account using their mobile device. This is a convenient and secure way to ensure that only the user has access to his or her account.
Conclusion
Cyber attacks cost businesses a lot of money. Cybercriminals have become more demanding in terms of monetary ransoms for data and businesses have no other choice but to comply. Security measures ensure that your data is safe and away from the prying hands of criminals.
Although these setting up these security measures comes with a price, it’s an investment that you will benefit from even years from now. It’s better to spend money on prevention than to lose money to reverse damages.
Read More:

Peyman Khosravani is a global blockchain and digital transformation expert with a passion for marketing, futuristic ideas, analytics insights, startup businesses, and effective communications. He has extensive experience in blockchain and DeFi projects and is committed to using technology to bring justice and fairness to society and promote freedom. Peyman has worked with international organizations to improve digital transformation strategies and data-gathering strategies that help identify customer touchpoints and sources of data that tell the story of what is happening. With his expertise in blockchain, digital transformation, marketing, analytics insights, startup businesses, and effective communications, Peyman is dedicated to helping businesses succeed in the digital age. He believes that technology can be used as a tool for positive change in the world.








